1
/
of
12
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
YY/T 0031-2008 English PDF (YY/T0031-2008)
YY/T 0031-2008 English PDF (YY/T0031-2008)
Regular price
$70.00
Regular price
Sale price
$70.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
YY/T 0031-2008: Silicone tubes and elastomeric parts for infusion and transfusion
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.Get Quotation: Click YY/T 0031-2008 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Newer / historical versions: YY/T 0031-2008
Preview True-PDF
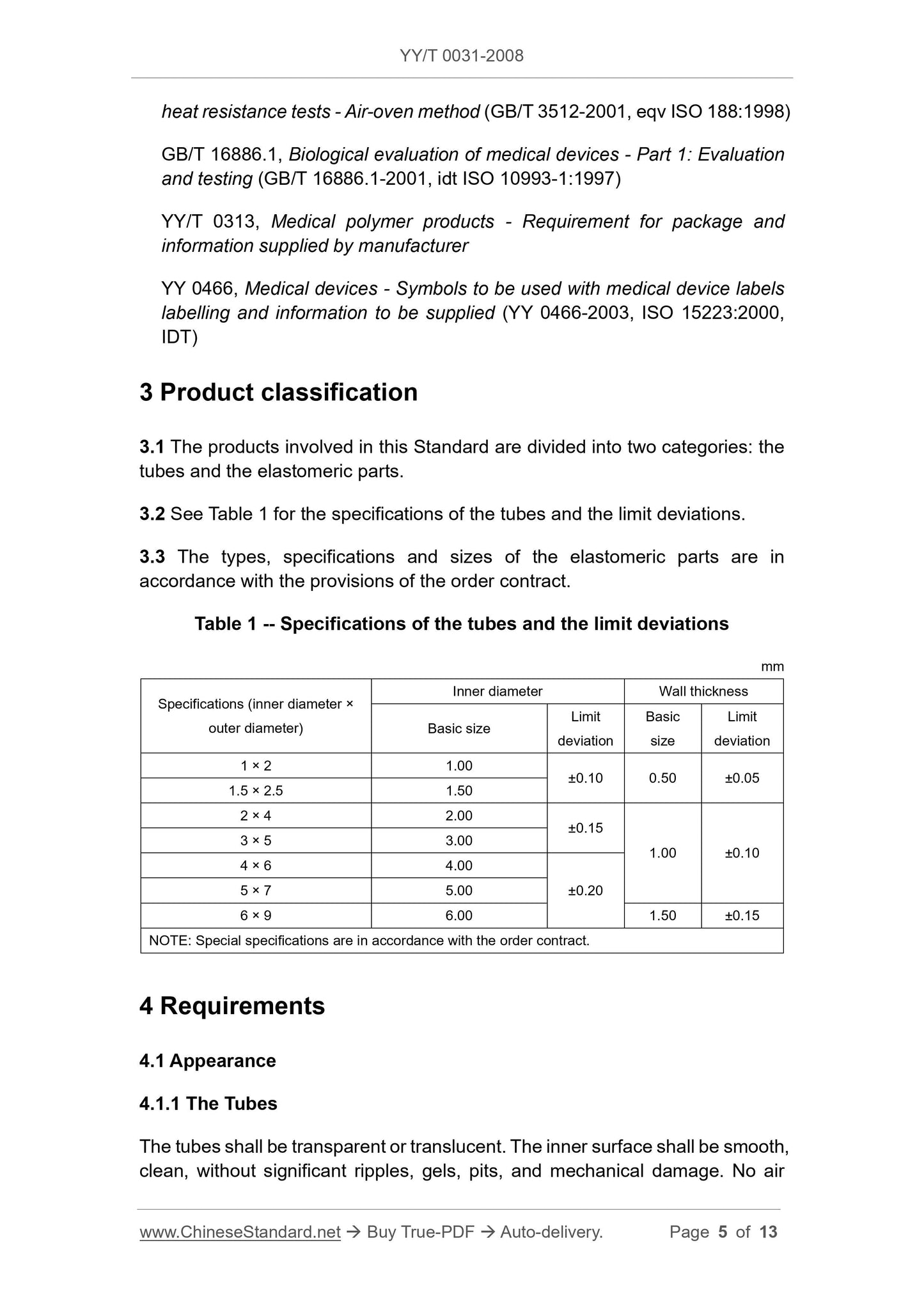
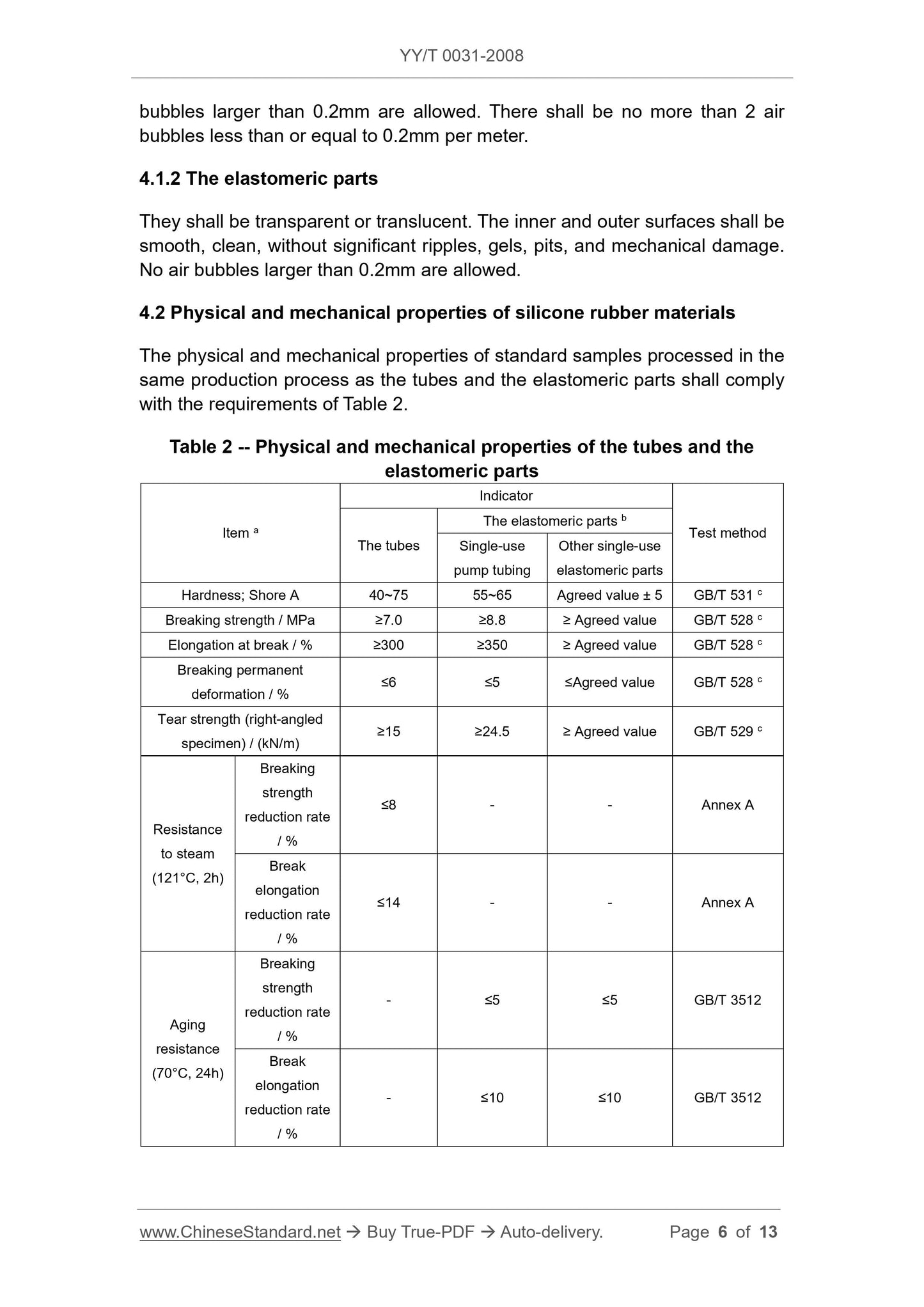
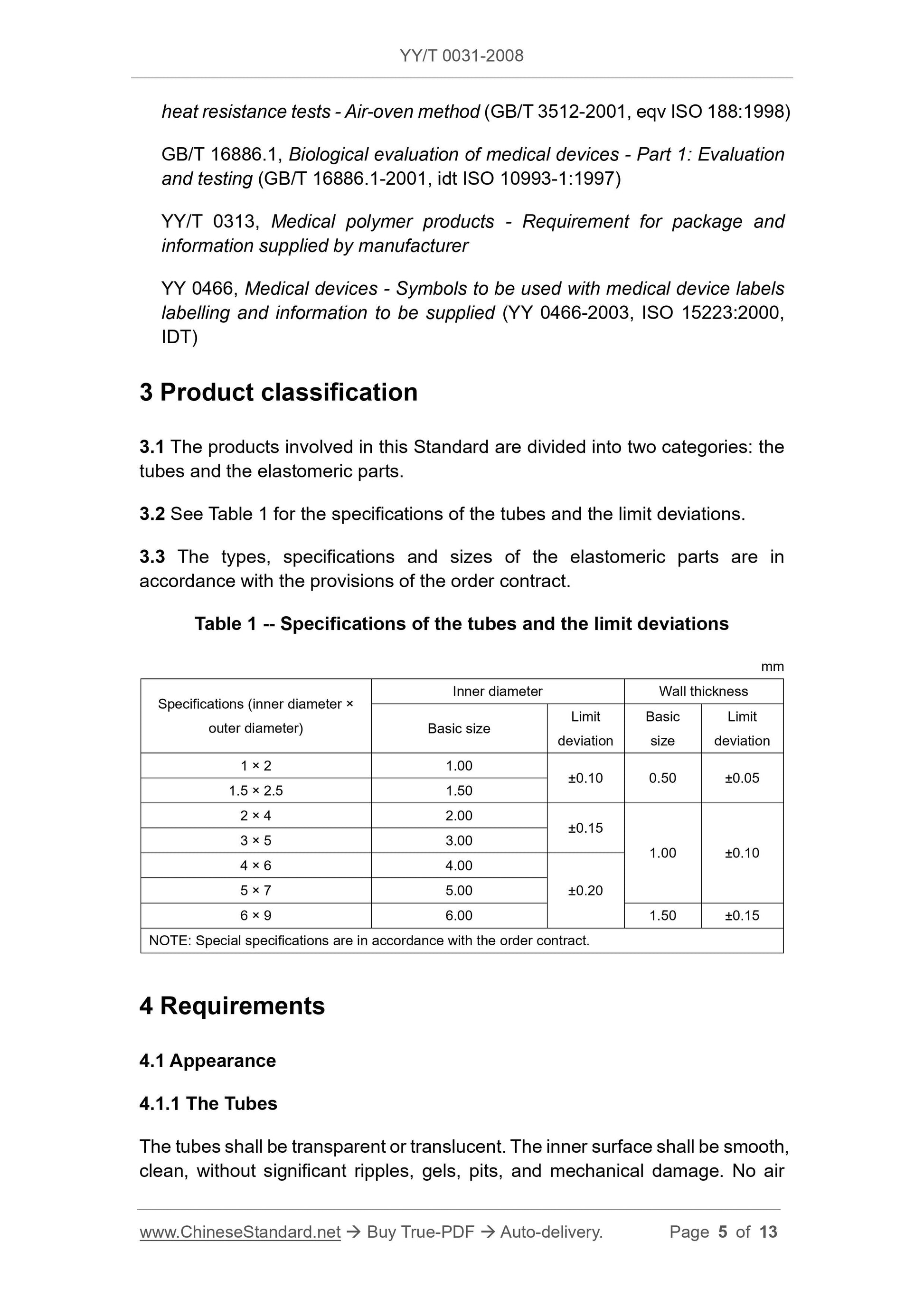
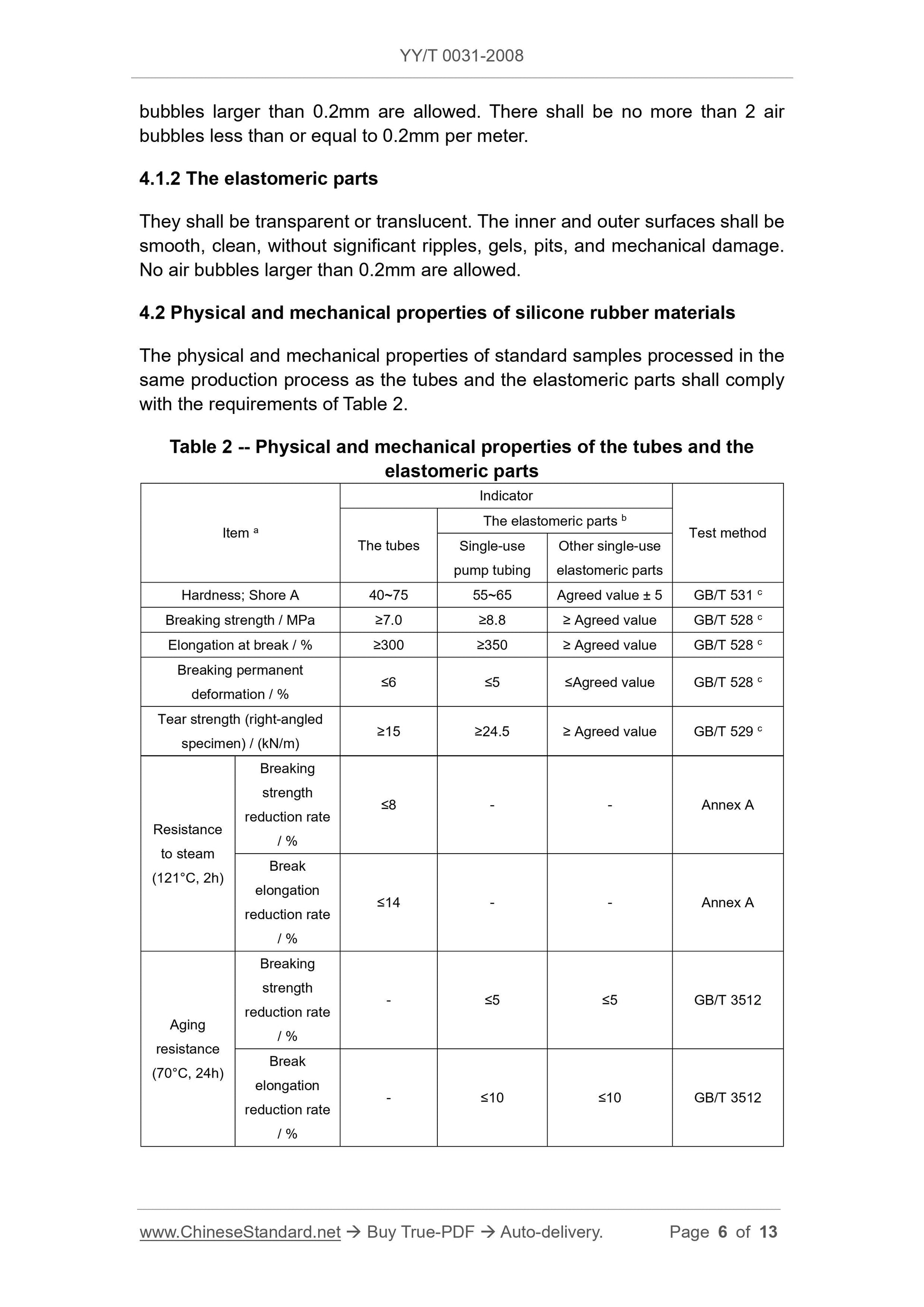
Scope
This Standard specifies the general requirements and test methods for siliconetubes for infusion and transfusion (hereinafter referred to as “the tubes”) and
elastomeric parts.
The products to which this Standard is applicable include (but are not limited
to):
-- Reusable in vitro transfer lines for intravenous infusion;
-- Disposable silicone rubber elastic parts in blood treatment products, such
as pump tubing, valves or seals for flow control devices, injection parts;
-- Silicone rubber elastic parts for disposable infusion apparatus, such as
silicone rubber reservoirs for injection parts and infusion pumps;
-- Pump tubes, valves, and injection parts in disposable pressure infusion
lines.
This Standard does not include silicone rubber catheters and artificial heart-
lung machine pump tubes inserted or implanted in the human body.
Basic Data
| Standard ID | YY/T 0031-2008 (YY/T0031-2008) |
| Description (Translated English) | Silicone tubes and elastomeric parts for infusion and transfusion |
| Sector / Industry | Medical Device and Pharmaceutical Industry Standard (Recommended) |
| Classification of Chinese Standard | G45 |
| Classification of International Standard | 11.040.20 |
| Word Count Estimation | 11,183 |
| Date of Issue | 2008-10-17 |
| Date of Implementation | 2010-01-01 |
| Older Standard (superseded by this standard) | YY 0031-1990 |
| Quoted Standard | GB/T 528; GB/T 529; GB/T 531; GB/T 3512; GB/T 16886.1; YY/T 0313; YY 0466 |
| Regulation (derived from) | SFDA [2008] No. 605 |
| Issuing agency(ies) | State Food and Drug Administration |
| Summary | This standard specifies the infusion, transfusion with silicone rubber tubing (hereinafter referred to as "piping") and the elastic member General requirements and test methods. This standard applies to products include (but not limited to): repetitive use of intravenous infusion of liquid transfer lines in vitro, disposable blood processing products silicone rubber elastic member, such as tubing, valves or flow control device seals, injection parts, etc., Disposable infusion set with silicone rubber elastic member, such as injection parts, infusion pumps and other silicone rubber storage sac, disposable pressure infusion pump tubing piping, valves, injection parts. This standard does not inserted or implanted in the body, including silicone rubber catheters and artificial heart-lung pump tube. |
Share