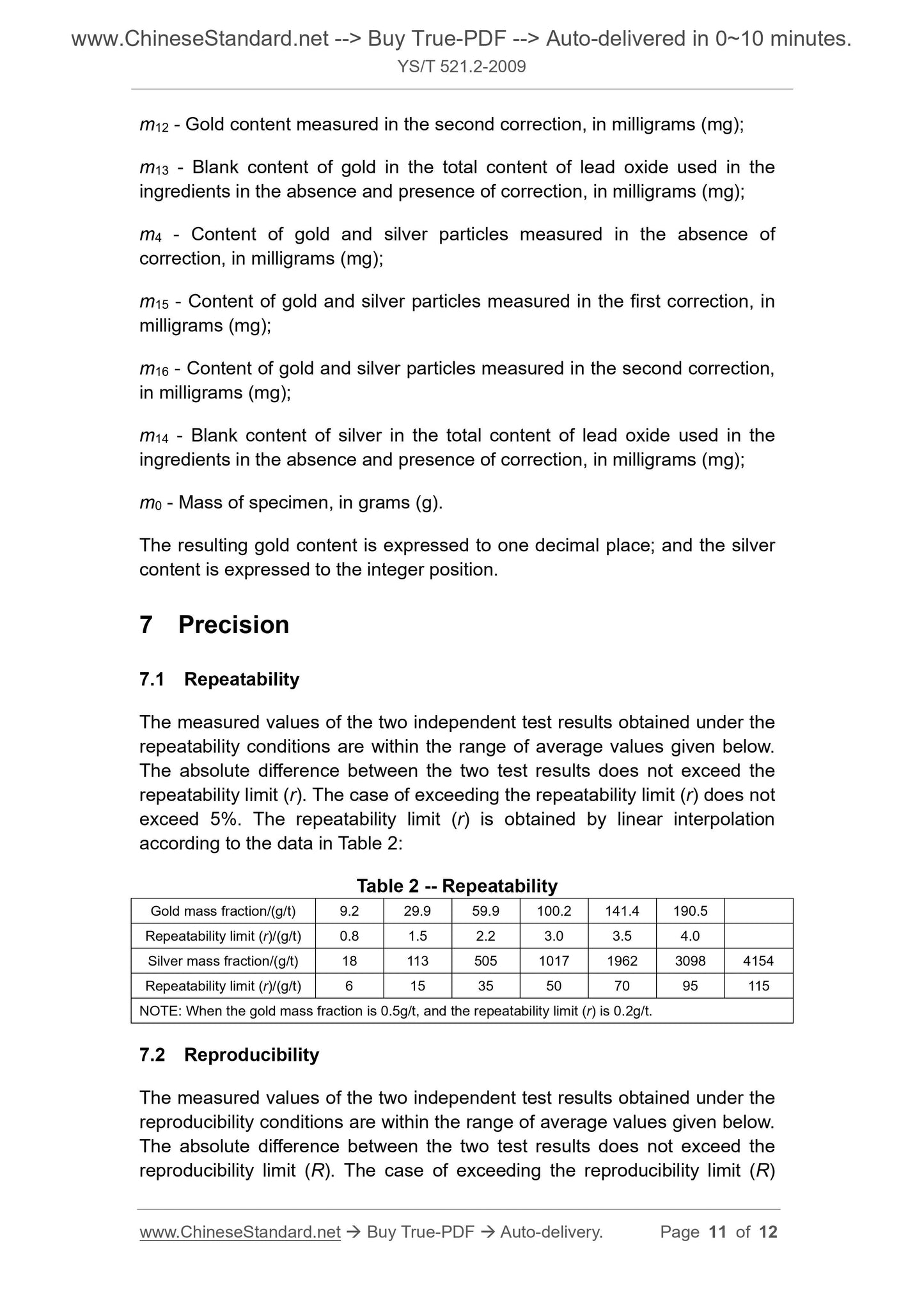
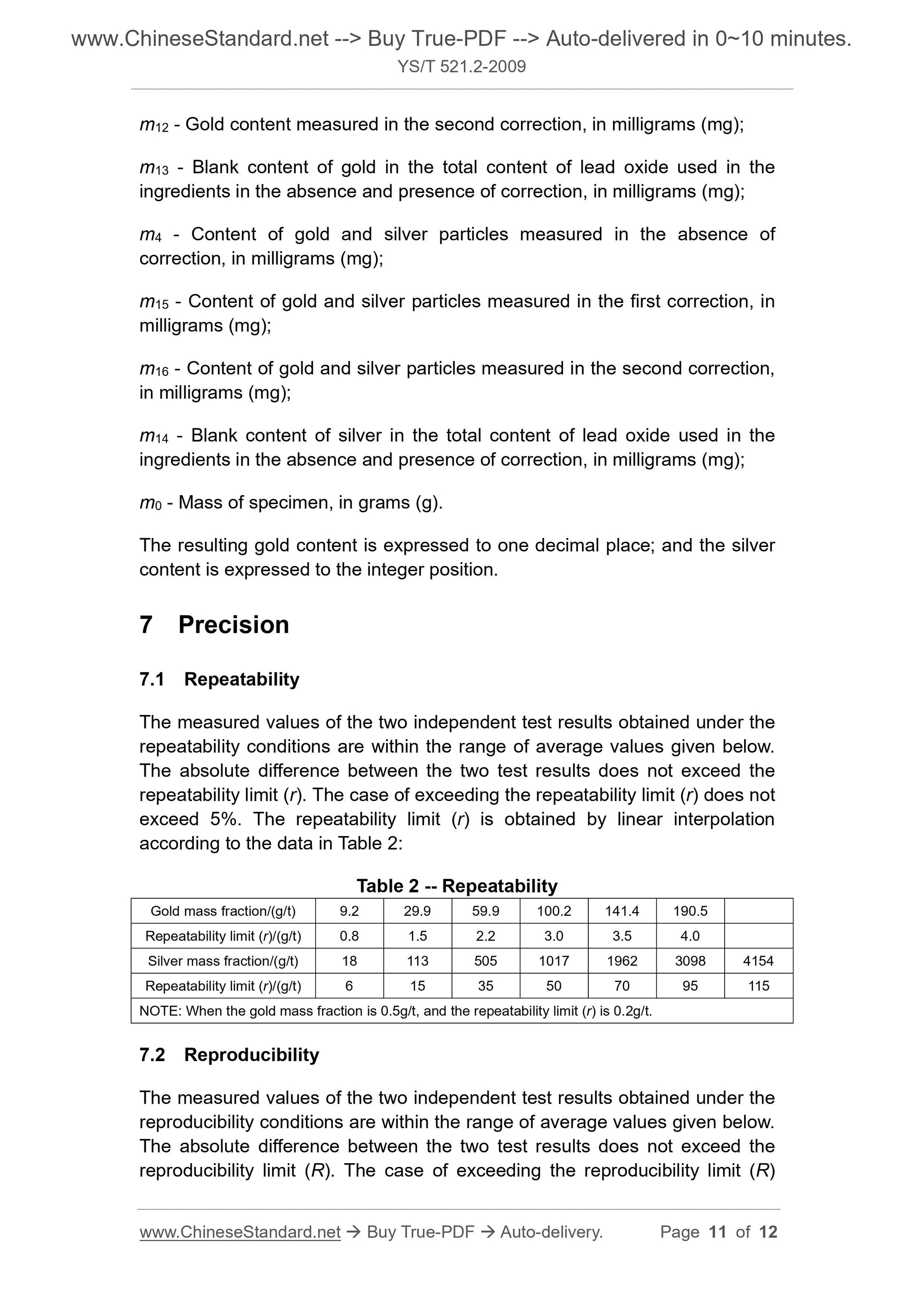
1
/
of
7
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
YS/T 521.2-2009 English PDF (YS/T521.2-2009)
YS/T 521.2-2009 English PDF (YS/T521.2-2009)
Regular price
$160.00
Regular price
Sale price
$160.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
YS/T 521.2-2009: Methods for chemical analysis of blister copper. Part 2: Determination of gold and silver contents. Fire assay method
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.Get Quotation: Click YS/T 521.2-2009 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Newer / historical versions: YS/T 521.2-2009
Preview True-PDF
Scope
This Part of YS/T 521 specifies the method for determining gold and silvercontents in blister copper.
This Part applies to the determination of gold and silver contents in blister
copper. Determination range. gold mass fraction ≥ 0.5g/t; silver mass fraction
≥ 20g/t.
Basic Data
| Standard ID | YS/T 521.2-2009 (YS/T521.2-2009) |
| Description (Translated English) | Methods for chemical analysis of blister copper. Part 2: Determination of gold and silver contents. Fire assay method |
| Sector / Industry | Nonferrous Metallurgy Industry Standard (Recommended) |
| Classification of Chinese Standard | H13 |
| Classification of International Standard | 77.120.30 |
| Word Count Estimation | 8,883 |
| Date of Issue | 2009-12-04 |
| Date of Implementation | 2010-06-01 |
| Older Standard (superseded by this standard) | YS/T 521.3-2006 |
| Regulation (derived from) | MIIT [2009] No. 66 |
| Issuing agency(ies) | Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
| Summary | This standard specifies the blister in the determination of the amount of gold and silver. This standard applies to blister copper gold and silver content. Measuring range: mass fraction of gold �� 0. 5g/t, silver mass fraction �� 20g/t. |
Share