1
/
of
8
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
SN/T 1004-2013 English PDF (SN/T1004-2013)
SN/T 1004-2013 English PDF (SN/T1004-2013)
Regular price
$120.00
Regular price
Sale price
$120.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
SN/T 1004-2013: Determination of urea residues in canned foods for export
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.Get Quotation: Click SN/T 1004-2013 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Newer / historical versions: SN/T 1004-2013
Preview True-PDF
Scope
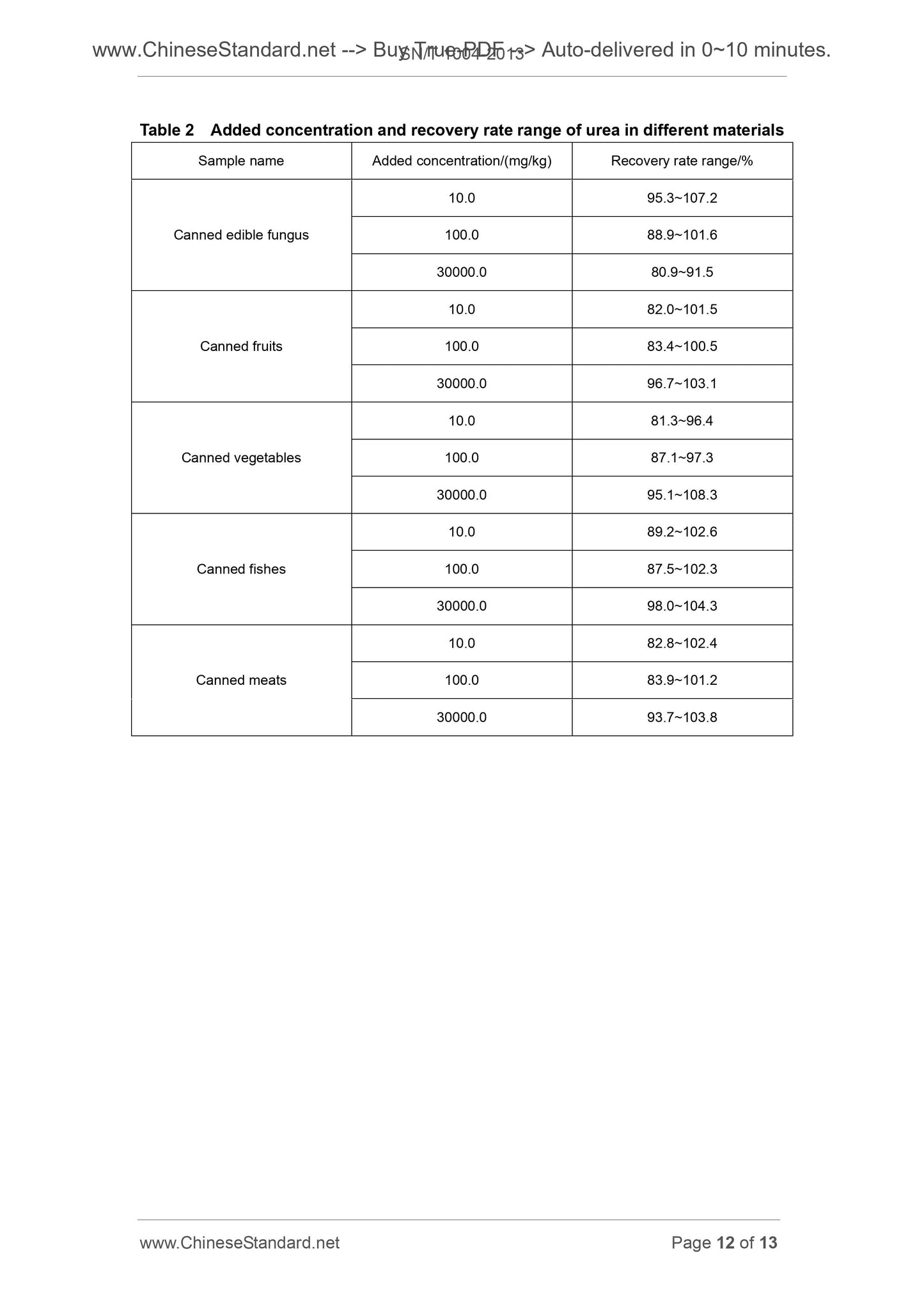
This Standard specifies the high performance liquid chromatography for determination ofurea residues in canned foods for export.
This Standard is applicable to determination of urea residues in canned edible fungus,
fruits, vegetables, fishes and meats.
Basic Data
| Standard ID | SN/T 1004-2013 (SN/T1004-2013) |
| Description (Translated English) | Determination of urea residues in canned foods for export |
| Sector / Industry | Commodity Inspection Standard (Recommended) |
| Classification of Chinese Standard | X79 |
| Classification of International Standard | 67.050 |
| Word Count Estimation | 13,168 |
| Older Standard (superseded by this standard) | SN/T 1004-2001 |
| Regulation (derived from) | National quality recognition (2013), No. 464; industry standard filing Notice No. 1 of 2014 (No. 169 overall) |
| Issuing agency(ies) | General Administration of Customs |
| Summary | This standard specifies the method of high performance liquid chromatography urea residues in canned foods. This standard applies to the determination of urea residues in edible mushrooms, fruits, vegetables, canned fish and meat. |
Share