1
/
of
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
QC/T 241-2011 English PDF (QC/T241-2011)
QC/T 241-2011 English PDF (QC/T241-2011)
Regular price
$260.00
Regular price
Sale price
$260.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
QC/T 241-2011: Air leakage test methods of automobile wheels for tubeless tires
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.Get Quotation: Click QC/T 241-2011 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Newer / historical versions: QC/T 241-2011
Preview True-PDF
Scope
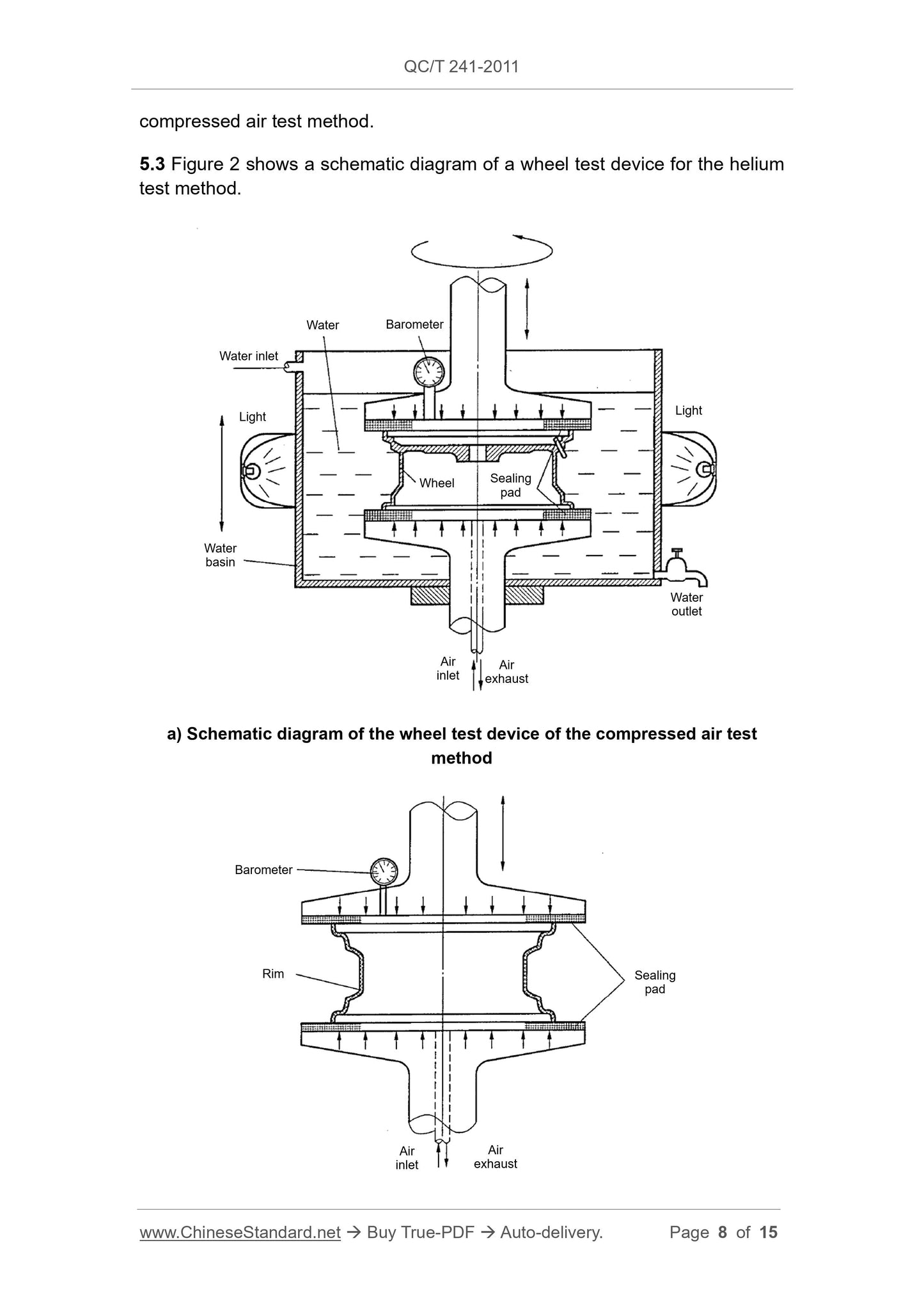
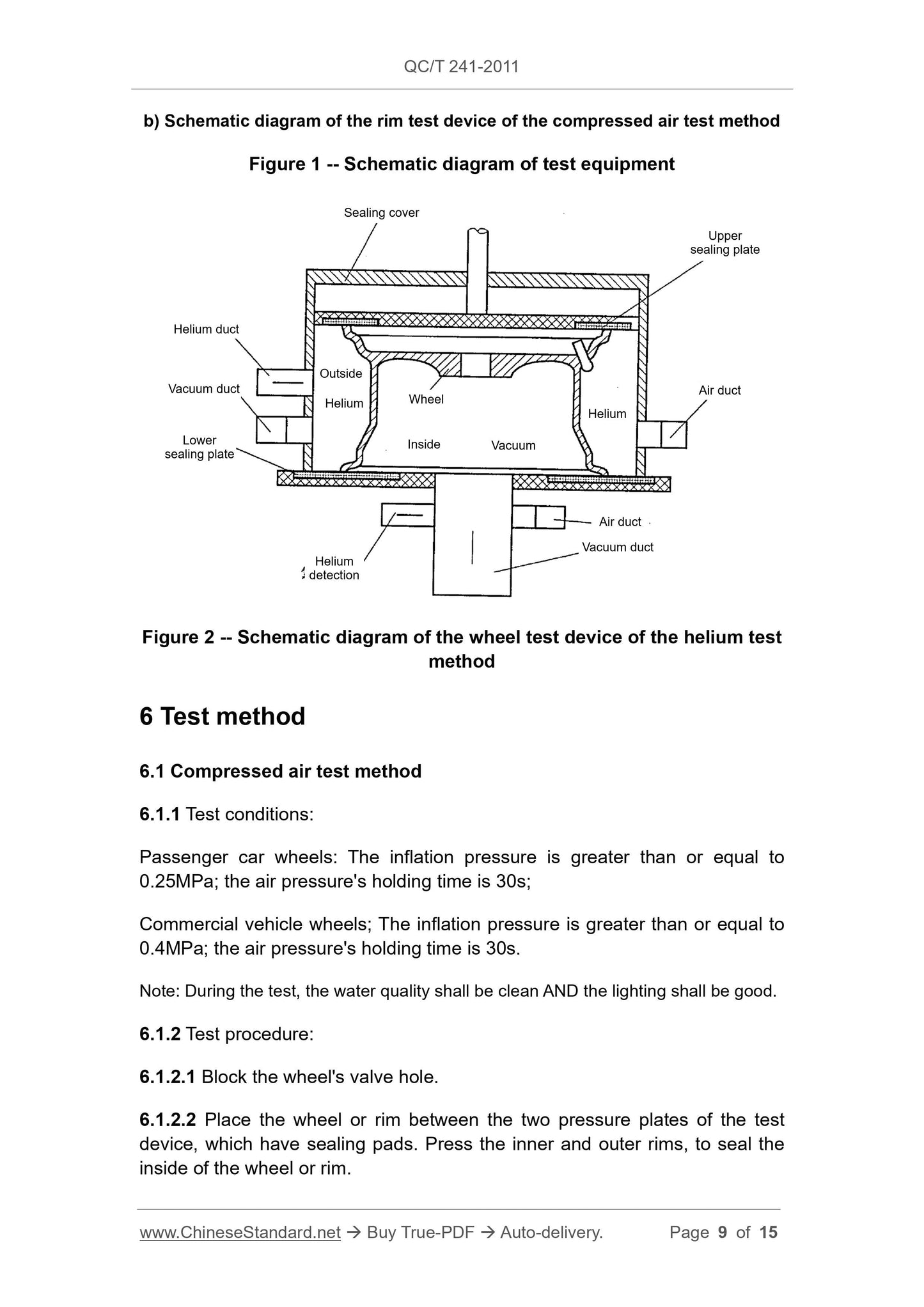
This standard specifies two test methods, for the air tightness of automobilewheels, namely the compressed air test method and the helium test method.
This standard applies to automobile wheels fitted with tubeless tires.
Basic Data
| Standard ID | QC/T 241-2011 (QC/T241-2011) |
| Description (Translated English) | Air leakage test methods of automobile wheels for tubeless tires |
| Sector / Industry | Automobile and Vehicle Industry Standard (Recommended) |
| Classification of Chinese Standard | T23 |
| Classification of International Standard | 43.040.50 |
| Word Count Estimation | 14,162 |
| Date of Issue | 2011-05-18 |
| Date of Implementation | 2011-08-01 |
| Older Standard (superseded by this standard) | QC/T 241-1997 |
| Quoted Standard | GB/T 2933 |
| Regulation (derived from) | Ministry of Industry and Information Technology Bulletin No. 13 of 2011 |
| Issuing agency(ies) | Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
| Summary | This standard specifies two car wheel tightness test methods, test method that compressed air and helium test method. This standard applies fitted with tubeless tires car wheels. |
Share