1
/
of
8
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
HJ 633-2012 English PDF
HJ 633-2012 English PDF
Regular price
$130.00
Regular price
Sale price
$130.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
HJ 633-2012: Technical Regulation on Ambient Air Quality Index (on trial)
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.Get Quotation: Click HJ 633-2012 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Newer / historical versions: HJ 633-2012
Preview True-PDF
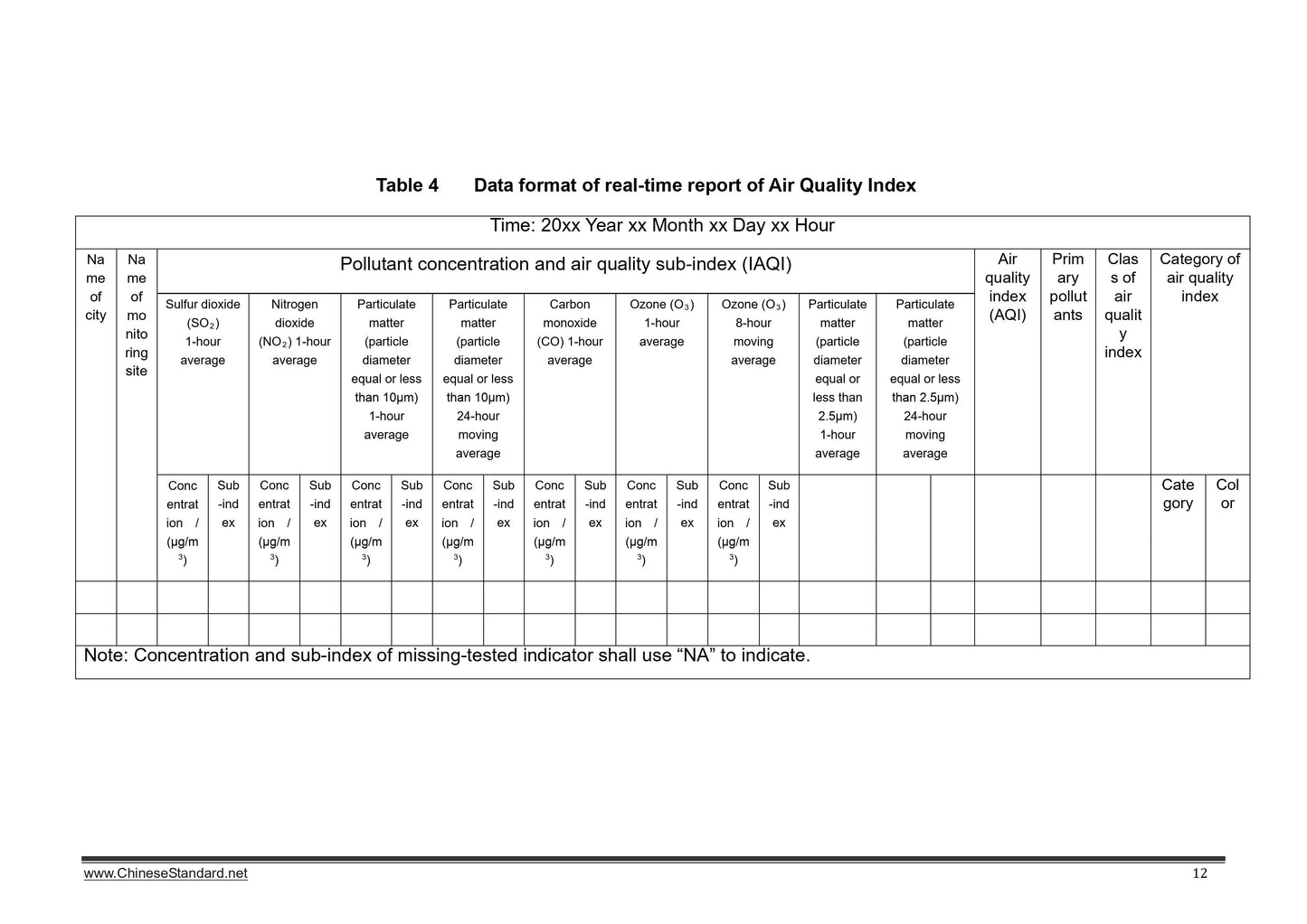
Scope
This Standard specifies classification scheme and calculation methods of ambient airquality index; ambient air quality levels and categories; and requirements of
publishing content of daily report and real-time report, publishing formats and other
relevant information of ambient air quality index.
This Standard applies to ambient air quality index’s daily report, real-time report and
forecasting, it is used to provide health advice to the public.
Basic Data
| Standard ID | HJ 633-2012 (HJ633-2012) |
| Description (Translated English) | Technical Regulation on Ambient Air Quality Index (on trial) |
| Sector / Industry | Environmental Protection Industry Standard |
| Classification of Chinese Standard | Z15 |
| Classification of International Standard | 13.040.20 |
| Word Count Estimation | 10,183 |
| Quoted Standard | GB 3095; HJ/T 193 |
| Regulation (derived from) | Department of Environmental Protection Notice 2012 No. 8; |
| Issuing agency(ies) | Ministry of Ecology and Environment |
| Summary | This standard specifies the ambient air quality index classification scheme, calculation methods and ambient air quality levels and categories, as well as real-time air quality index daily newspaper and publishing content, publishing formats and other rel |
Share