1
/
of
10
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
GB/T 5137.2-2002 English PDF (GB/T5137.2-2002)
GB/T 5137.2-2002 English PDF (GB/T5137.2-2002)
Regular price
$85.00
Regular price
Sale price
$85.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
GB/T 5137.2-2002: Test methods of safety glazing materials used on road vehicles -- Part 2: optical properties tests
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.Get Quotation: Click GB/T 5137.2-2002 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Newer / historical versions: GB/T 5137.2-2002
Preview True-PDF
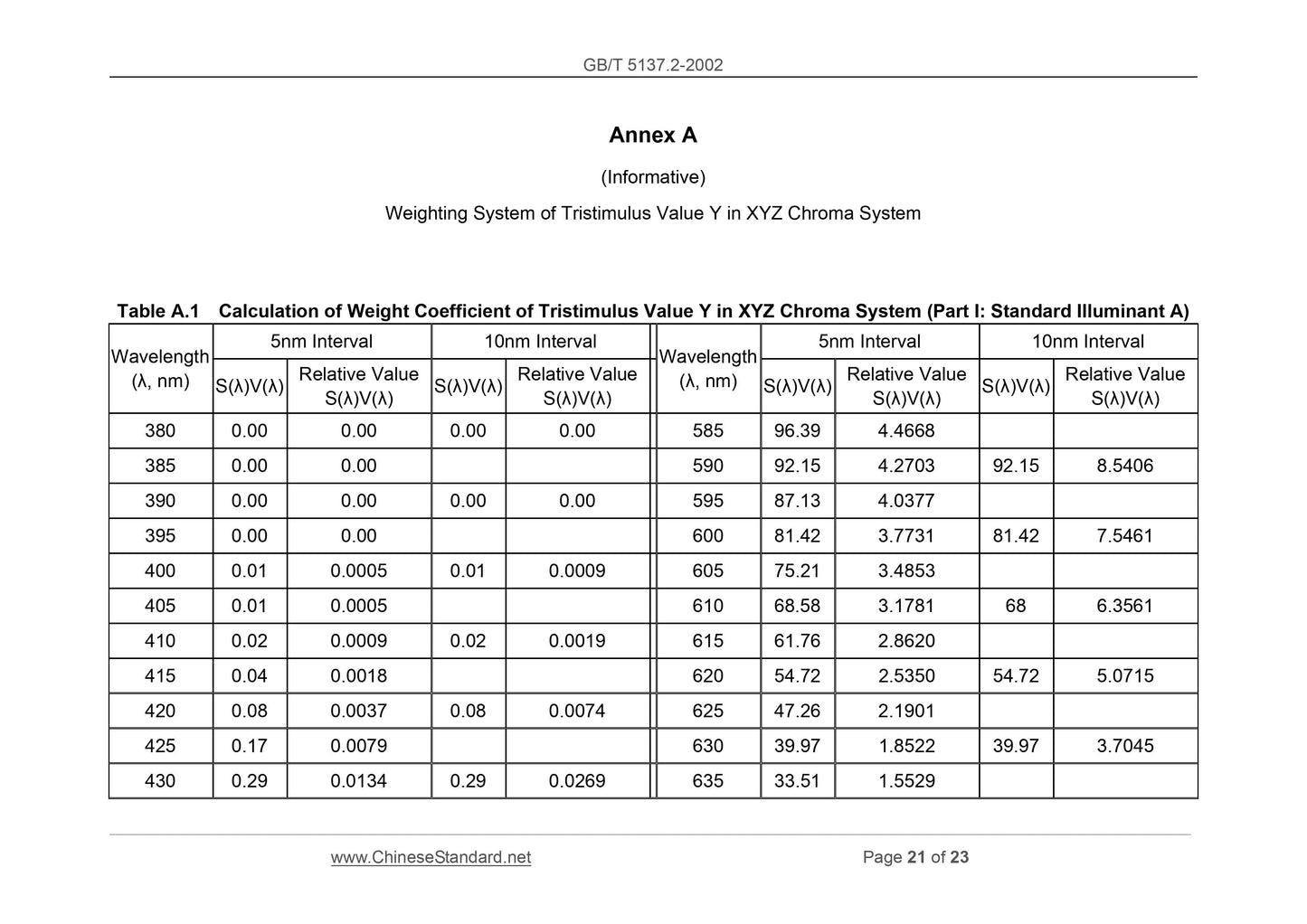
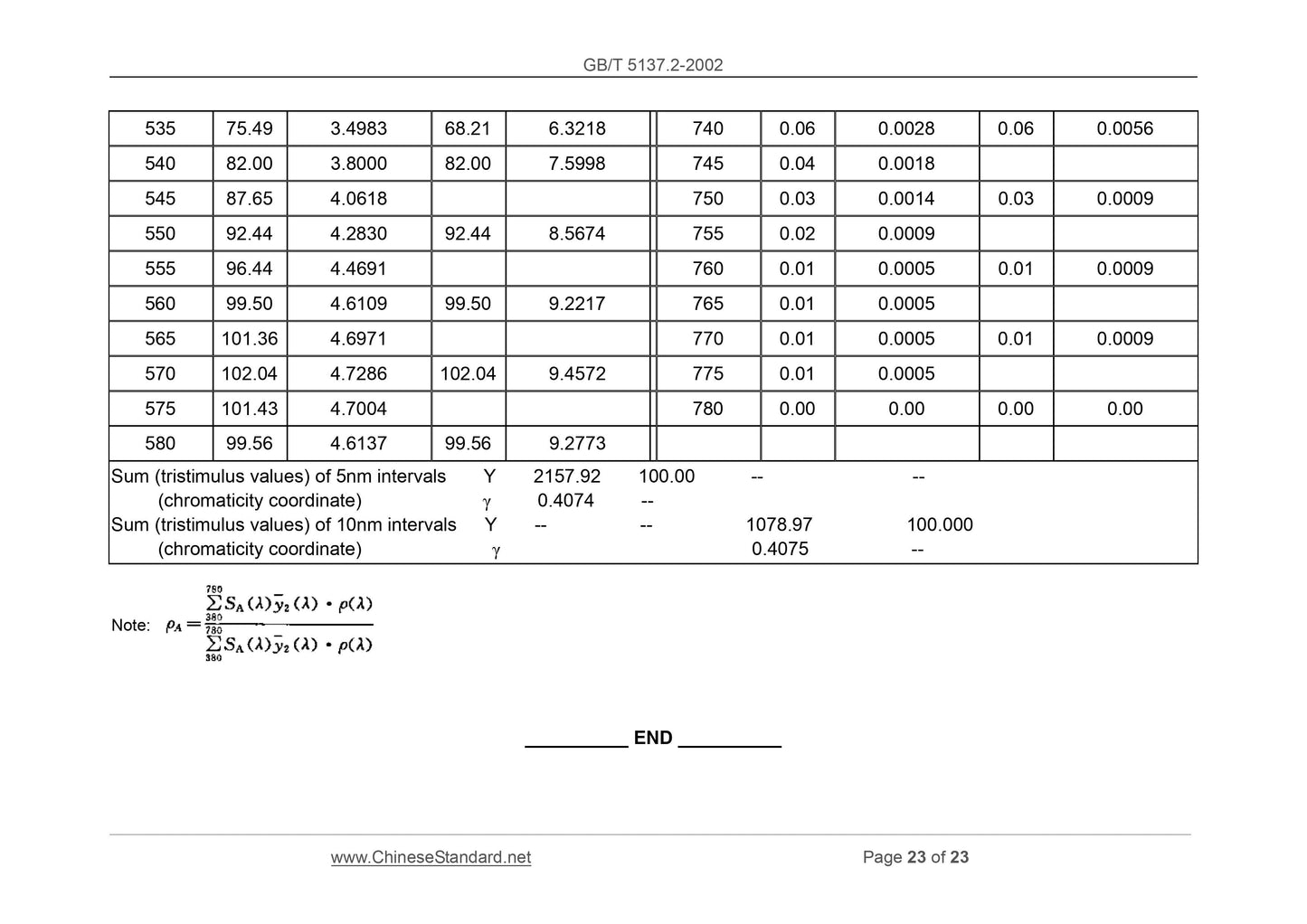
Scope
This Part of GB/T 5137 specifies the test method for the optical properties ofsafety glass used for road vehicles.
This Part is applicable for the road vehicle safety glass (hereinafter referred to
as safety glass). The safety glass includes glass products processed from all
kinds of glass OR the combination of the glass and other materials.
Basic Data
| Standard ID | GB/T 5137.2-2002 (GB/T5137.2-2002) |
| Description (Translated English) | Test methods of safety glazing materials used on road vehicles - Part 2: optical properties tests |
| Sector / Industry | National Standard (Recommended) |
| Classification of Chinese Standard | Q34 |
| Classification of International Standard | 81.040.30 |
| Word Count Estimation | 15,151 |
| Date of Issue | 2002-12-20 |
| Date of Implementation | 2003-05-01 |
| Older Standard (superseded by this standard) | GB/T 5137.2-1996 |
| Adopted Standard | ISO 3538-1997; MOD |
| Issuing agency(ies) | General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People Republic of China |
| Summary | This standard specifies the: automotive safety glass Test methods for optical properties. This standard applies to: automotive safety glass (hereinafter referred to as safety glass). This includes all types of safety glass glass processed into or a combination of glass and other materials into glass products. |
Share