1
/
of
5
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
GB/T 36381-2018 English PDF (GB/T36381-2018)
GB/T 36381-2018 English PDF (GB/T36381-2018)
Regular price
$150.00
Regular price
Sale price
$150.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
GB/T 36381-2018: Classification of Liquid Chemical Waste
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.Get Quotation: Click GB/T 36381-2018 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Newer / historical versions: GB/T 36381-2018
Preview True-PDF
Scope
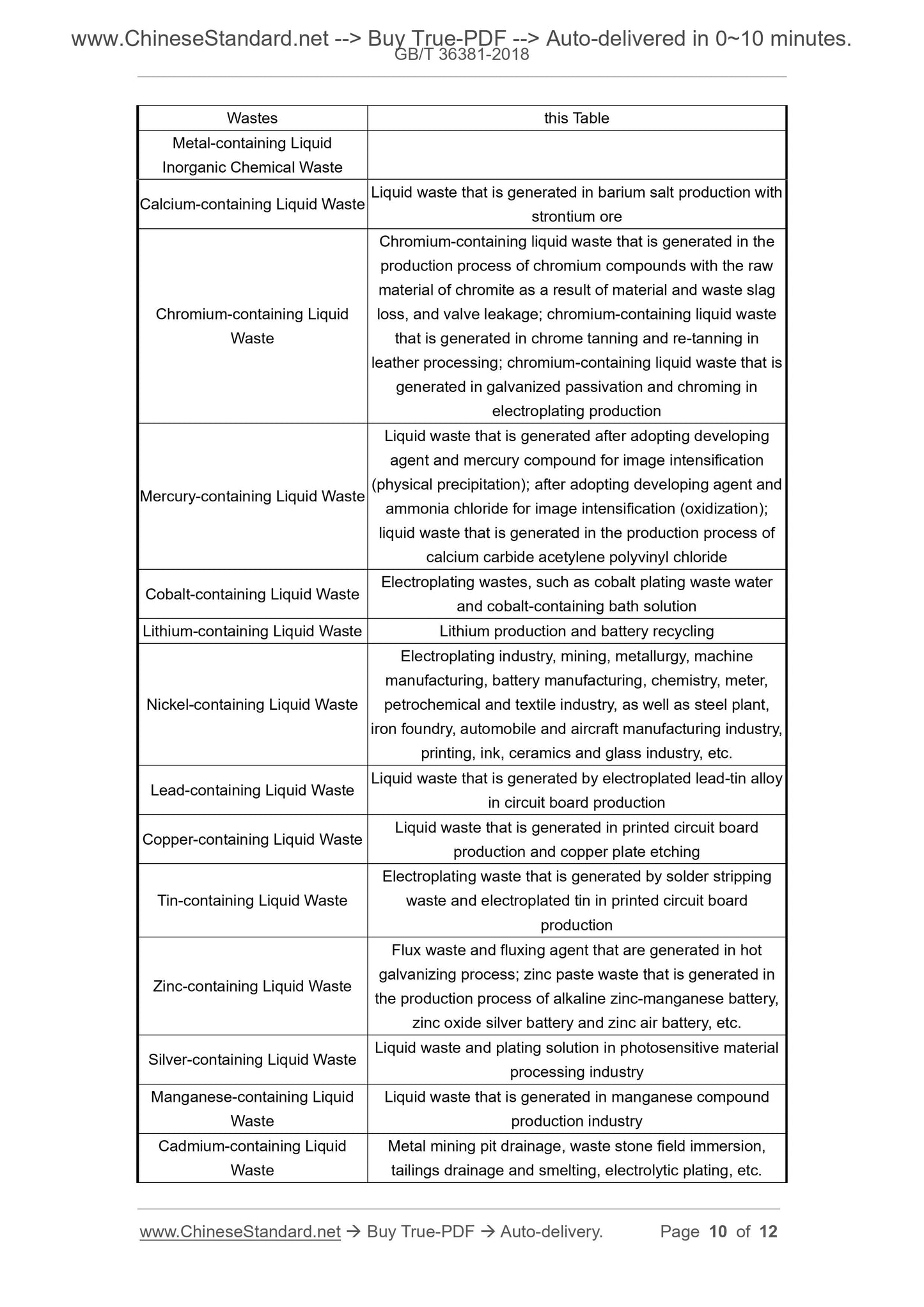
This Standard specifies the terms, definitions, classification method, classification,code and requirements of liquid chemical waste.
This Standard is applicable to producers and professional disposal institutes of liquid
chemical waste in the classification and resource recycling of liquid chemical waste.
This Standard is not applicable to liquid chemical waste generated in laboratories,
medical treatment and pharmaceuticals, and radioactive liquid chemical waste.
Basic Data
| Standard ID | GB/T 36381-2018 (GB/T36381-2018) |
| Description (Translated English) | Classification of Liquid Chemical Waste |
| Sector / Industry | National Standard (Recommended) |
| Classification of Chinese Standard | Z04 |
| Classification of International Standard | 13.030.01 |
| Word Count Estimation | 10,114 |
| Date of Issue | 2018-06-07 |
| Date of Implementation | 2019-01-01 |
| Issuing agency(ies) | State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration |
Share