1
/
of
5
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
GB/T 33216-2016 English PDF (GB/T33216-2016)
GB/T 33216-2016 English PDF (GB/T33216-2016)
Regular price
$150.00
Regular price
Sale price
$150.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
GB/T 33216-2016: Steel Open Die Forgings on Hammer - Classification of Complexity and Equivalent Coefficient
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.Get Quotation: Click GB/T 33216-2016 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Newer / historical versions: GB/T 33216-2016
Preview True-PDF
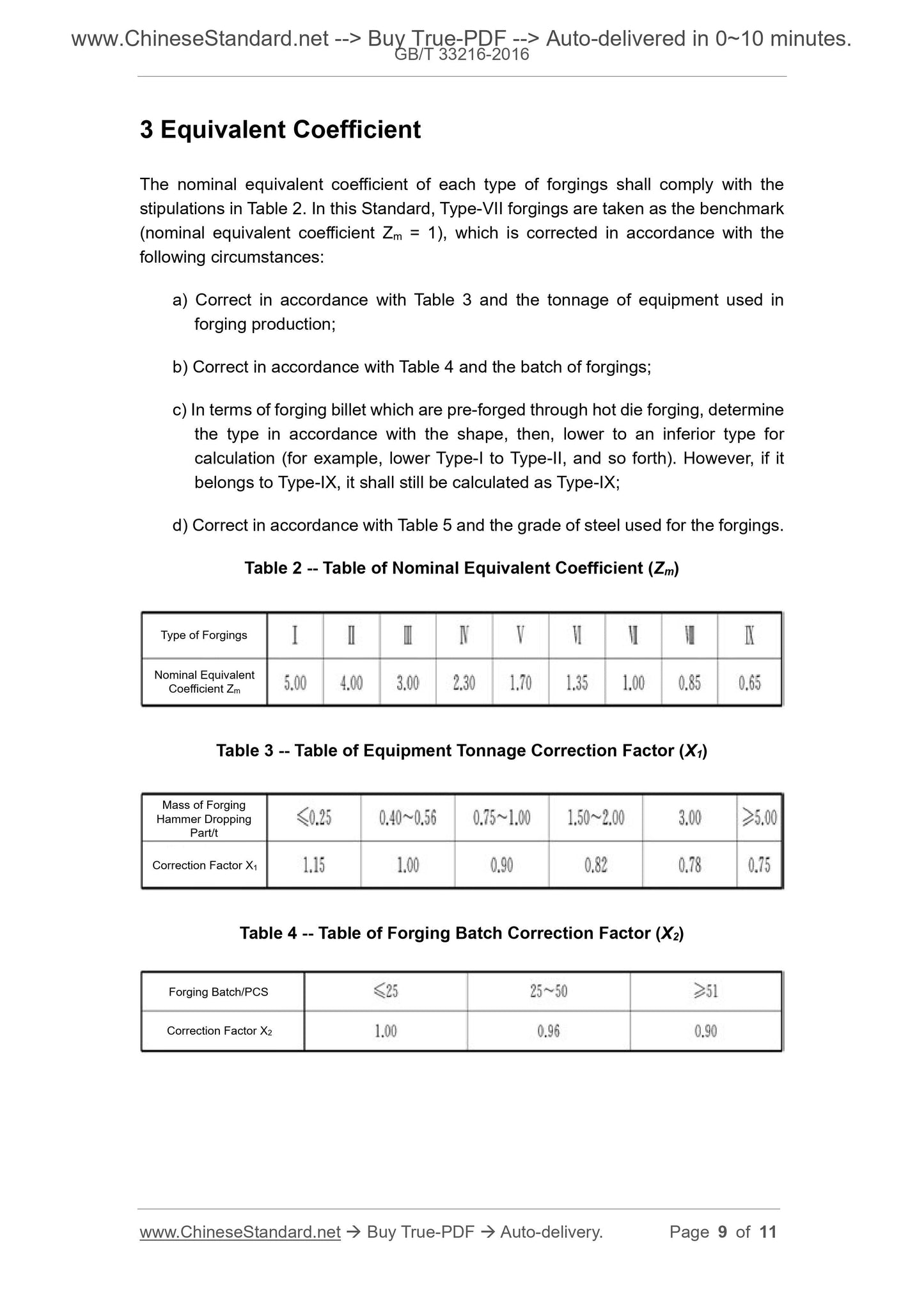
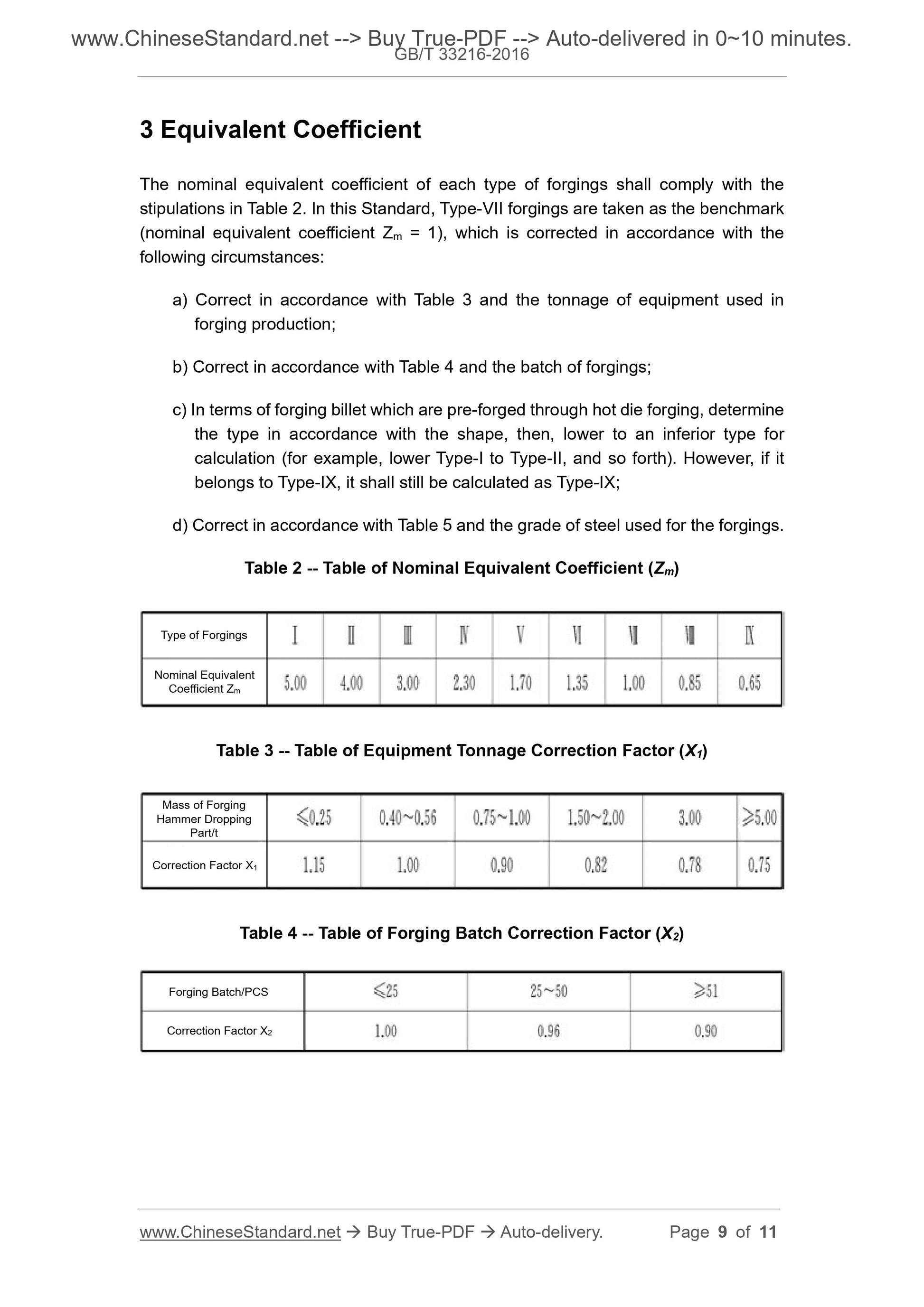
Scope
This Standard stipulates the classification of complexity and equivalent coefficient forsteel open die forgings on hammer.
This Standard is applicable to general-purpose carbon-steel and structural alloy-steel
open die forgings (including tire die forgings) on hammer.
This Standard may be considered as a basis for the statistics of the standard
production volume of forgings, and the formulation of production quota and energy
consumption. In addition, it may also be considered as a reference for enterprises in
the formulation of sale price.
Basic Data
| Standard ID | GB/T 33216-2016 (GB/T33216-2016) |
| Description (Translated English) | Steel Open Die Forgings on Hammer - Classification of Complexity and Equivalent Coefficient |
| Sector / Industry | National Standard (Recommended) |
| Classification of Chinese Standard | J32 |
| Classification of International Standard | 77.140.85 |
| Word Count Estimation | 10,160 |
| Date of Issue | 2016-12-13 |
| Date of Implementation | 2017-07-01 |
| Regulation (derived from) | National Standard Notice No.156 of 2016 |
| Issuing agency(ies) | General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China |
Share