1
/
of
7
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
GB/T 14849.4-2014 English PDF (GB/T14849.4-2014)
GB/T 14849.4-2014 English PDF (GB/T14849.4-2014)
Regular price
$130.00
Regular price
Sale price
$130.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
GB/T 14849.4-2014: Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part 4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric method
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.Get Quotation: Click GB/T 14849.4-2014 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Newer / historical versions: GB/T 14849.4-2014
Preview True-PDF
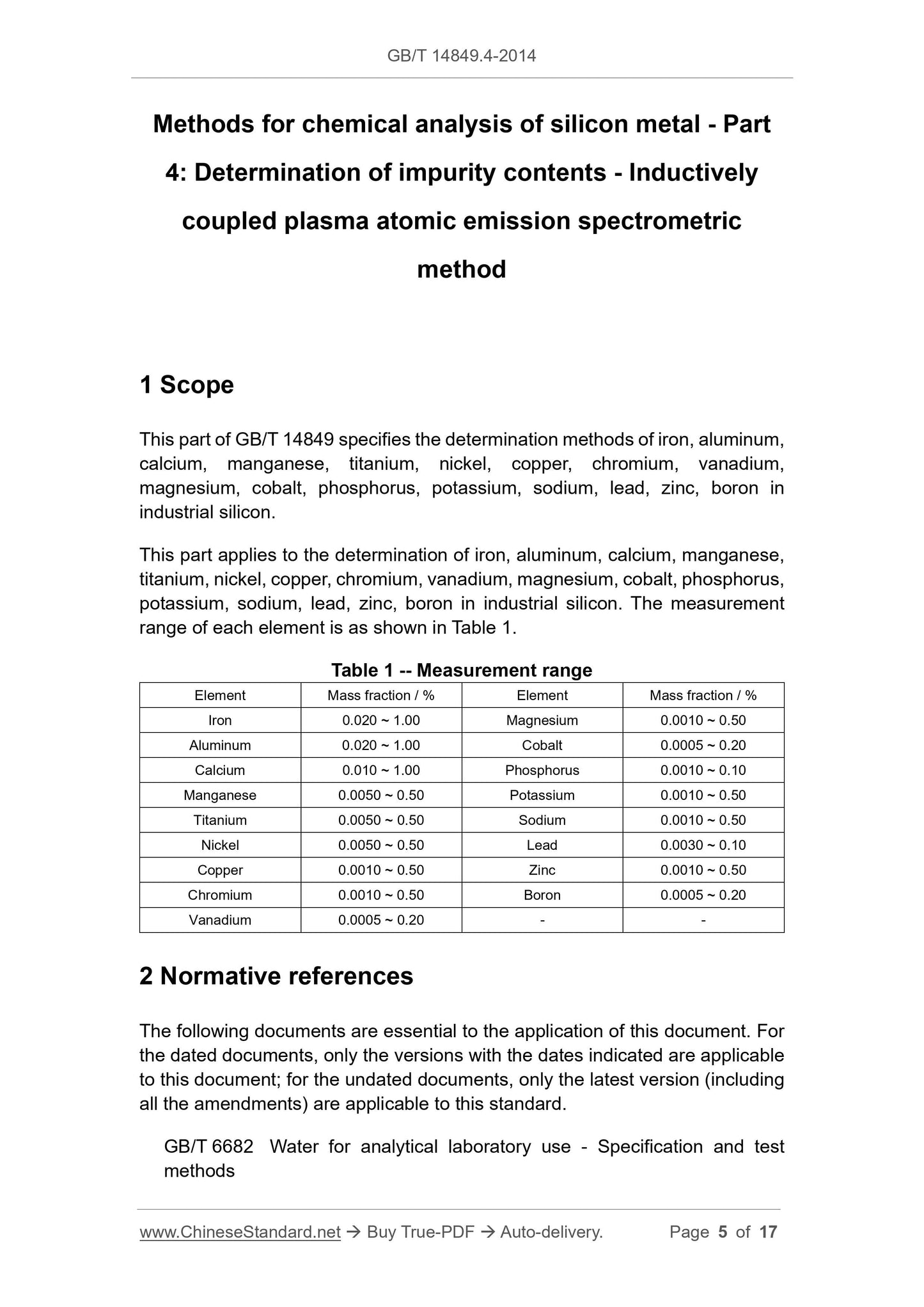
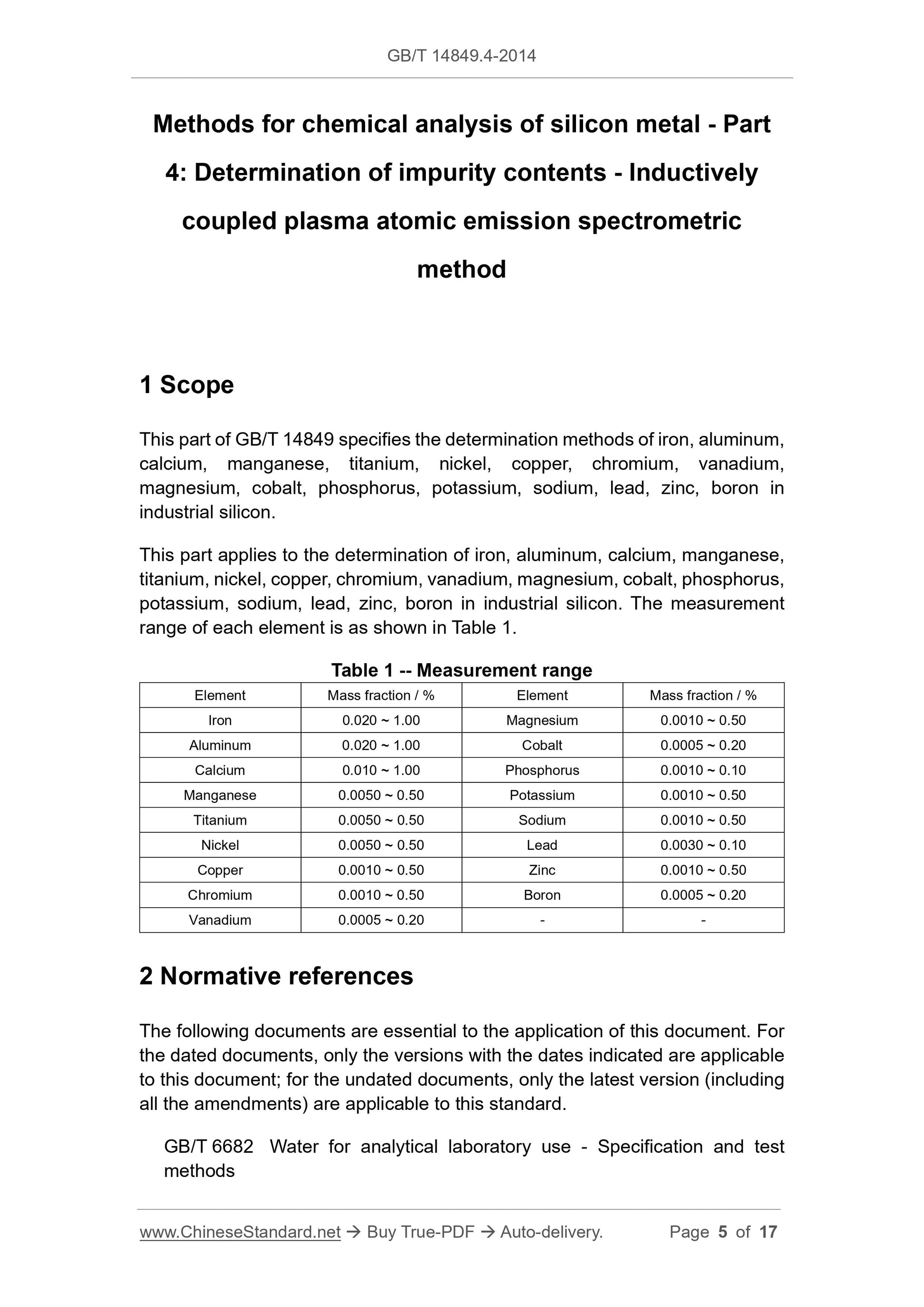
Scope
This part of GB/T 14849 specifies the determination methods of iron, aluminum,calcium, manganese, titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium,
magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in
industrial silicon.
This part applies to the determination of iron, aluminum, calcium, manganese,
titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus,
potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in industrial silicon. The measurement
range of each element is as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 -- Measurement range
Element Mass fraction / % Element Mass fraction / %
Iron 0.020 ~ 1.00 Magnesium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Aluminum 0.020 ~ 1.00 Cobalt 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Calcium 0.010 ~ 1.00 Phosphorus 0.0010 ~ 0.10
Manganese 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Potassium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Titanium 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Sodium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Nickel 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Lead 0.0030 ~ 0.10
Copper 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Zinc 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Chromium 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Boron 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Vanadium 0.0005 ~ 0.20 - -
Basic Data
| Standard ID | GB/T 14849.4-2014 (GB/T14849.4-2014) |
| Description (Translated English) | Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part 4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric method |
| Sector / Industry | National Standard (Recommended) |
| Classification of Chinese Standard | H12 |
| Classification of International Standard | 77.120.10 |
| Word Count Estimation | 13,164 |
| Date of Issue | 12/5/2014 |
| Date of Implementation | 8/1/2015 |
| Older Standard (superseded by this standard) | GB/T 14849.4-2008 |
| Quoted Standard | GB/T 6682; GB/T 8170 |
| Regulation (derived from) | Announcement of Newly Approved National Standards 2014 No. 27 |
| Issuing agency(ies) | General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China |
| Summary | This Standard specifies industrial silicon iron, aluminum, calcium, manganese, iron, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium, manganese, cobalt, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron content determination. This Standard is applicable to the iron, al |
Share